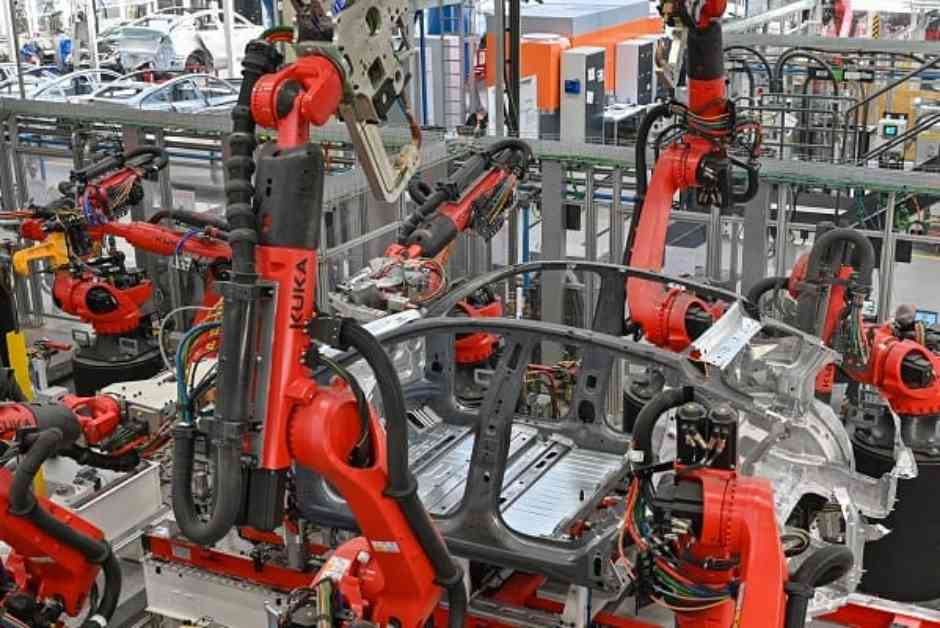
Mass production has revolutionized the manufacturing industry by enabling the production of large quantities of plastic and metal parts in a relatively short amount of time. This process is essential for meeting the growing needs of customers in industries such as consumer electronics and automotive parts. Understanding the intricacies of mass production and the techniques involved is crucial for manufacturers looking to streamline their production processes and remain competitive in the market.
Understanding Mass Production
Mass production refers to the production of a large number of standardized products within a short time frame. The key procedures involved in mass production include the assembly line and the use of mechanical equipment to streamline the manufacturing process. The primary objective of mass production is to produce a high volume of units with consistent quality standards and cost-effective pricing. This is particularly important in industries where demand for parts is high, such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, and consumer goods.
Techniques in Mass Production
1. **Injection Molding**:
Injection molding is a widely used method for producing plastic parts in high volumes. This process involves injecting hot plastic into a mold, where it cools and hardens into the desired shape. Injection molding is highly efficient as it allows for rapid production of large quantities of parts while minimizing material waste and production time.
2. **Stamping and Forging for Metals**:
Stamping and forging are commonly used techniques for manufacturing metal parts in mass production. Stamping involves using a die to shape a metal sheet into a specific form, while forging uses heat and pressure to shape metal into the desired shape. Both stamping and forging offer precision and consistency, making them ideal for high-volume production processes.
3. **CNC Machining**:
CNC machining is a versatile tool that can be used for both plastic and metal parts manufacturing. This process involves using automated tools to remove material from workpieces based on programmed instructions. CNC machining offers high precision and accuracy, making it suitable for producing intricate designs in high volumes.
Advantages of Mass Production
1. **Economies of Scale**:
Mass production enables manufacturers to achieve economies of scale by spreading fixed costs over a large number of units. This leads to a reduction in the cost per unit, making products more affordable for consumers.
2. **Consistency and Quality**:
Mass production ensures consistent quality across all units by using automated processes and standardized procedures. This reliability is crucial in industries where precision and safety are paramount.
3. **Speed and Efficiency**:
High-volume production allows companies to manufacture products quickly and efficiently, enabling them to meet deadlines and fulfill market demands promptly.
The Future of Mass Production
Technological advancements continue to shape the future of mass production, with additive manufacturing (3D printing) emerging as a viable option for producing metal and plastic parts. 3D printing allows for the rapid creation of designs in small quantities, reducing waste material and increasing flexibility in production processes.
Additionally, the integration of Industry 4.0 principles such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming high-volume production processes. Smart factories equipped with real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance capabilities are enhancing resource efficiency by minimizing downtime and maximizing overall productivity.
In conclusion, mass production plays a crucial role in modern manufacturing industries by enabling the efficient production of large quantities of plastic and metal parts. Understanding the techniques involved, leveraging technological advancements, and embracing Industry 4.0 principles are essential for manufacturers looking to stay competitive in a rapidly evolving market.